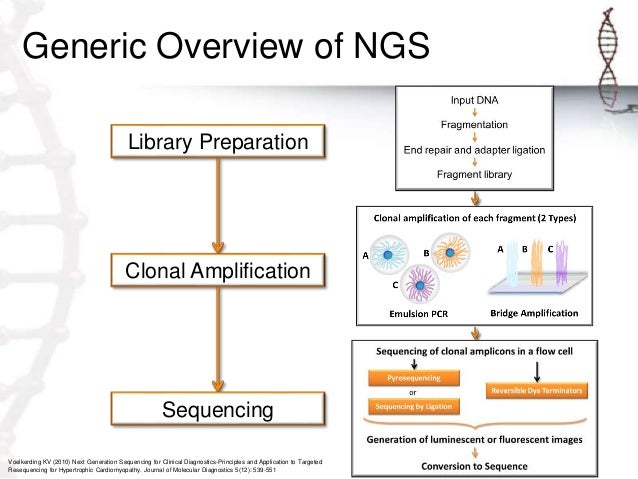
Next Generation Sequencing Ngs

Following the completion of the human genome project, the high demand for low-cost sequencing has given rise to a number of high-throughput, next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies. These new sequencing platforms allow high-throughput sequencing for a wide range of applications such as: Next.
Next generation sequencing ngs. ASM NGS Conference Goes Virtual! After thoughtful consideration, ASM has made the difficult decision to cancel the in-person ASM Conference on Rapid Applied Microbial Next-Generation Sequencing and Bioinformatic Pipelines (NGS), scheduled to take place Oct. 23-26, 2020, in Washington, D.C. Next generation sequencing (NGS) is becoming a predominant tool in answering a broad range of biological questions. Its popularity can be attributed to its cost-effectiveness, its broad utility, and its multiplexing capabilities, which can be used to sequence hundreds, if not thousands, of individual libraries simultaneously [].Because library preparation is step-intensive and cumbersome. Next-generation sequencing involves three basic steps: library preparation, sequencing, and data analysis. Find resources to help you prepare for each step and see an example workflow for microbial whole-genome sequencing, a common NGS application. Learn More Next-generation sequencing (NGS)-based molecular tests have revolutionized the practice of medicine with the ability to personalize diagnosis, risk assessment, and treatment of patients with cancer and non-neoplastic disorders. Given the vast amounts of quantitative and complex sequencing data generated by high-throughput sequencers, clinical.
The massively parallel sequencing technology known as next-generation sequencing (NGS) has revolutionized the biological sciences. With its ultra-high throughput, scalability, and speed, NGS enables researchers to perform a wide variety of applications and study biological systems at a level never before possible. NEXT GENERATION SEQUENCING (NGS) Whether it’s your first next generation sequencing project or your hundredth, GENEWIZ scientists are dedicated to helping you find the right NGS solution for your research. We have spent years optimizing our processes to deliver the highest quality results that meet your budget and deadline. Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) The first major foray into DNA sequencing was the Human Genome Project. This project, which used first-generation sequencing, known as Sanger sequencing (the chain-termination method), took 13 years, cost $3 billion and was completed in 2003. The completion of the Human Genome Project in 2003 ushered in a new era of rapid, affordable, and accurate genome analysis—called Next Generation Sequencing (NGS). NGS builds upon 'first generation sequencing' technologies to yield accurate and cost-effective sequencing results. Fred Sanger sequenced the first whole DNA genome, the virus phage ?X174, in 1977.
Global Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) Services Market, by Service Type: 1.1 Targeted Resequencing & Custom Gene Panels 1.2 RNA-Seq 1.3 De Novo Sequencing 1.4 Exome Sequencing 1.5 Chip-Seq 1.6. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) applications have been transitioning from research tools to diagnostic methods and are becoming more commonplace in clinical microbiology laboratories. These applications include (1) whole-genome sequencing, (2) targeted next-generation sequencing methods, and (3) metagenomic next-generation sequencing. Next-generation sequencing (NGS), also known as high-throughput sequencing, is the catch-all term used to describe a number of different modern sequencing technologies including: Illumina (Solexa) sequencing Roche 454 sequencing Ion torrent: Proton / PGM sequencing SOLiD sequencing These recent technologies allow us to sequence DNA and RNA much more quickly and cheaply than the previously used. Next generation sequencing has become a commodity. With the commercialization of various affordable desktop sequencers, NGS has become within the reach of traditional wet-lab biologists. As seen in recent years, genome-wide scale computational analysis is increasingly being used as a backbone to foster novel discovery in biomedical research.
Ancestry ® Launches AncestryHealth ® Powered by Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) Next generation sequencing offers more comprehensive data on more commonly inherited health conditions. Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) has become a key analysis method for biological research, enabling researchers to obtain a global view of biological processes. Advice and guidance for sequencing projects are offered by our team, which relies on more than 10 years of experience with sequencing systems, high-throughput data analysis, and cutting. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) is a high-throughput methodology that enables rapid sequencing of the base pairs in DNA or RNA samples. Supporting a broad range of applications, including gene expression profiling, chromosome counting, detection of epigenetic changes, and molecular analysis, NGS is driving discovery and enabling the future of personalized medicine. Whether you are new to next-generation sequencing (NGS) or want to learn about the various applications of NGS, we have the learning materials to help you understand the technology and get started quickly. NGS is a high-throughput method achieved by sequencing clonally amplified DNA templates on a massively parallel scale.
Massive parallel sequencing or massively parallel sequencing is any of several high-throughput approaches to DNA sequencing using the concept of massively parallel processing; it is also called next-generation sequencing (NGS) or second-generation sequencing.Some of these technologies emerged in 1994-1998 and have been commercially available since 2005. Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) is a powerful platform that has enabled the sequencing of thousands to millions of DNA molecules simultaneously. Next-generation sequencing (NGS), also known as high-throughput sequencing, is the catch-all term used to describe a number of different modern sequencing technologies. Vela Diagnostics provides a Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) solution* that is simple, fast, and affordable -- putting the power of NGS technology in the reach of labs of all sizes. The solution is easy-to-use, from automated template preparation and library construction, to sequencing, data analysis and reporting. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) is a term used for describing a range of various modern sequence technology, also known as high-throughput sequencing. These technologies enable DNA and RNA to be sequenced much faster and cheaper than the Sanger sequence used before.
1 Definition. Next generation sequencing, kurz NGS, ist eine verbesserte Technologie zur DNA-Sequenzierung.Sie erlaubt im Gegensatz zur Sanger-Sequenzierung höhere Geschwindigkeiten: Ein komplettes, menschliches Genom kann innerhalb eines Tages sequenziert werden.. 2 Hintergrund. Vorherige Methoden beruhen entweder auf enzymatischen (Sanger-Sequenzierung) oder chemischen (Maxam-Gilbert.